Key Challenges
SARMENTI addresses the following key challenges:
Improve selectivity, sensitivity, precision and fabrication cost of existing state-of-the-art sensors, while maintaining their functionality for a long period of use either in the soil or in the air. The partners bring to the project different cutting-edge electrochemical sensors (nanowire and potentiometric) sensitive to the concentration of soil nutrients in a liquid. They also bring environmental sensors, especially to measure the concentration of gases released in the bio-chemical cycle of natural manure. These sensors require advances to enable real time in situ soil nutrients analysis;
Integration of the sensors in a multi-sensor frontend module able to monitor different nutrients or environmental parameters and placed for long periods of time (ideally whole crop duration) in difficult outdoor conditions and even buried in the case of the Soil Probe;
Packaging to increase the lifetime of the sensors, to efficiently sample the soil moisture or the surrounding air and decrease the system power consumption;
Guarantee the integrity of electronic components and data against attempts to bring down or take advantage of the system in an unauthorized manner, by the development of a secure IoT node and its integration with secure connectivity.
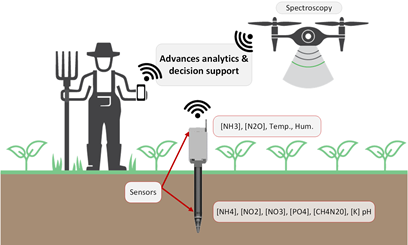
Sarmenti system
The development of the SARMENTI system requires the integration of inter-disciplinary knowledge from a manifold of enabling principles including nanoelectronics, electrochemistry, micro-electro-mechanics, bio-systems technologies, chemistry, data analytics, communication technologies, embedded software and edge computing, cyber-security for the IoT.
The envisioned architecture for the SARMENTI node consists of three devices:
the Soil Probe buried in the soil. It will contain electrochemical sensors in a hygroscopic membrane to monitor soil nutrient concentration. It will also contain pH, moisture and temperature sensors;
the Air Probe monitors the gases in the environment surrounding the Soil Probe and other environmental conditions (e.g. temperature, humidity, UV). It will be located just above the ground;
the Smart Data Logger collects data from both probes and transmits them directly to the cloud.